What is a cardiac cycle?
It is the process between the end of one heartbeat and the beginning of the next. Cardiac cycle overview: Heart performance As we all know, the heart is a muscular organ with four chambers. Now we will see how these four chambers work together to produce a heartbeat.
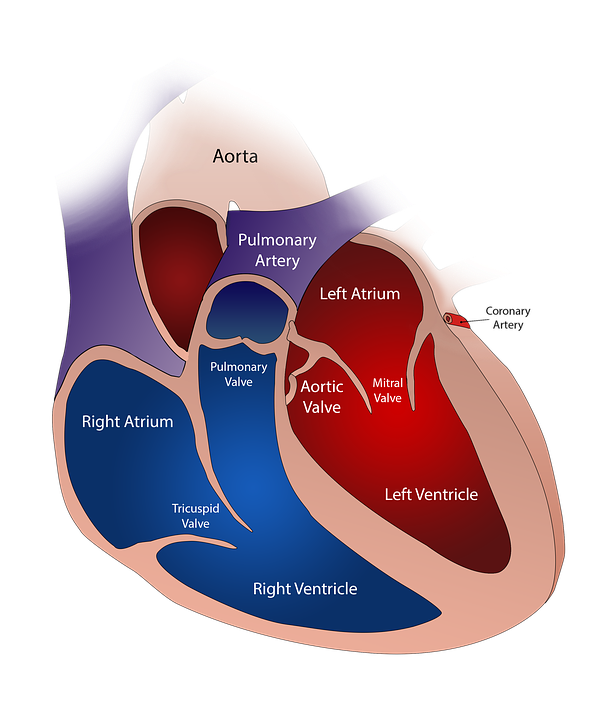
The figure above shows the anatomy of a normal heart. The two chambers in the upper part are the atria, and the two lower chambers are the ventricles. These atria and ventricles’ rhythmic contraction and relaxation cause the sound lub-dub, i.e., the beating sound.
The contraction and relaxation process is divided into 2 phases, systole and diastole. The systole and diastole of the heart are crucial for the blood pressure.
When blood is pumped out of the chambers, it is called systole, and the pressure that occurs creating this contraction is called systolic pressure.
When the Cardiac cycle overview Heart performance relaxes and allows blood to flow in, it is called diastole, and the pressure created is called diastolic pressure.
This is divided into four processes that affect each chamber of the heart.
Atrial systole
when the atrium is filled with blood, the atrium contracts. This pressure causes the atrioventricular valves, such as the tricuspid and bicuspid valves, to open and blood to enter the ventricle. The th3en ventricle is approximately 70 to 80% full of blood.
Ventricular Systole
In this phase, the ventricle is filled with more blood and contracts, but there is not enough pressure to push the blood out of the heart. However, this can cause blood to mix in the atrium and ventricle, which is caused by the valves closing (The tricuspid and bicuspid valves). Thus, blood is pumped out of the ventricle after sufficient pressure.
Ventricular diastole
The relaxation of the ventricle. The blood in the ventricle has been expelled and is now relaxing. The pressure generated during contraction decreases dramatically, resulting in a dip in the ECG of the heartbeat. The semilunar valve is now closed to prevent backflow of blood as blood now enters the ventricle following the atrial contraction that occurred at the same time.
Atrial diastole
During this phase, the atrium fills with blood. The atrioventricular valve is open, while the semilunar valve has been closed to prevent the backflow of blood, in the sense that the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is prevented.
All processes occur simultaneously. When the atrium contracts, the ventricle relaxes, and vice versa.
Summary
The process described above applies only to one heartbeat. The heart is an organ that amazes me every time with its fast and constant work. The heart will always be an inspiration and a motivation to work hard without expecting anything in return.
Naturally keeping the heart healthy
Symptoms and causes of a heart attack
Amazing fact about human heart: heart anatomy